-
Research Paper
-
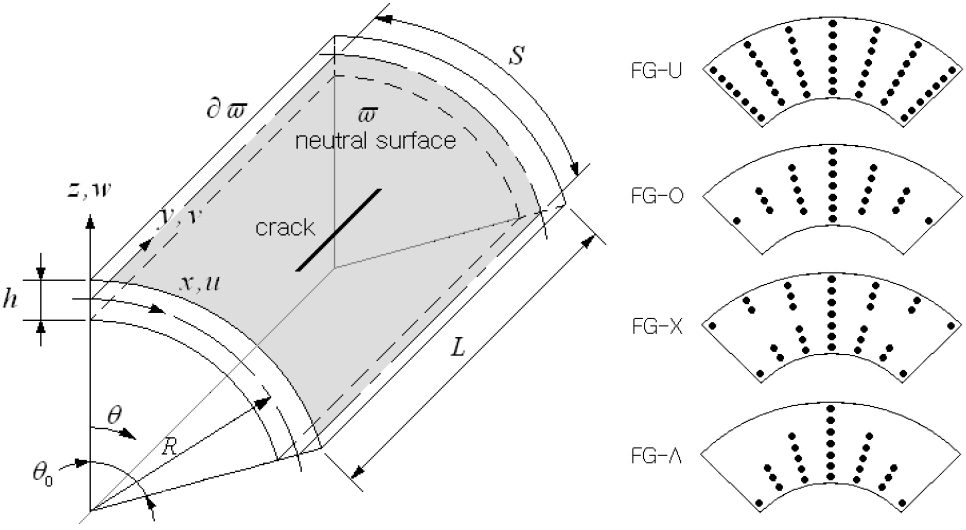
Numerical Buckling Analysis of Cracked Graphene-Reinforced Cylindrical Structures using a Phase-Field Crack Formulation
위상필드 균열 정식화를 이용한 그래핀이 강화된 원통형 구조물의 좌굴 수치해석
-
Jin-Rae Cho
조진래
- This study presents a numerical investigation of the buckling load of a cracked cylindrical panel reinforced with graphene platelets (GPLs). An effective …
본 논문은 그래핀 혈소판(GPL)으로 보강되고 내부 균열을 가진 원통 복합 구조물에 대한 임계 좌굴하중의 수치적 고찰을 다루고 있다. 임계 좌굴하중을 정확하게 평가하기 …
- This study presents a numerical investigation of the buckling load of a cracked cylindrical panel reinforced with graphene platelets (GPLs). An effective phase-field crack model was incorporated into the framework of the 2-D natural element method (NEM) to accurately evaluate the buckling loads of graphene-reinforced panels. Graphene platelets were introduced into a cracked cylindrical panel according to a prescribed functional distribution pattern throughout the thickness. Conventional crack node separation methods for representing cracks are not only difficult but also prone to numerical inaccuracy and instability. To overcome this limitation, the proposed phase-field model represents crack initiation using a phase-field value without grid manipulation. The numerical stability of the developed crack model was verified through a convergence test with respect to the grid density and comparison with a reference solution. A detailed parametric study was then conducted to examine the influence of key parameters on the buckling load characteristics.
- COLLAPSE
본 논문은 그래핀 혈소판(GPL)으로 보강되고 내부 균열을 가진 원통 복합 구조물에 대한 임계 좌굴하중의 수치적 고찰을 다루고 있다. 임계 좌굴하중을 정확하게 평가하기 위해 이차원 자연요소법(NEM) 기반으로 개발한 효과적인 위상필드 균열모델을 제시하였다. 그래핀 혈소판은 두께방향으로 특정한 기능적 분포패턴으로 원통형 구조물에 삽입되어 있다. 수치적으로 균열의 존재를 표현하는 전통적인 절점분리 기법은 모델링의 번거로움은 물론 수치적 불안정성을 야기할 수 있다. 이러한 문제점을 극복하기 위해 본 논문에서의 위상필드 정식화에서는 수치 그리드의 복잡한 작업 없이 위상 필드를 도입하여 균열을 표현하였다. 개발된 수치기법의 안정성과 신뢰성은 그리드 밀도에 따른 수렴성과 참고문헌과의 비교를 통해 입증하였으며, 그래핀이 보강된 원통 복합재의 좌굴특성을 관련된 주요 인자들에 따른 파라메트릭 수치실험을 통해 고찰하였다.
-
Numerical Buckling Analysis of Cracked Graphene-Reinforced Cylindrical Structures using a Phase-Field Crack Formulation
-
Research Paper
-
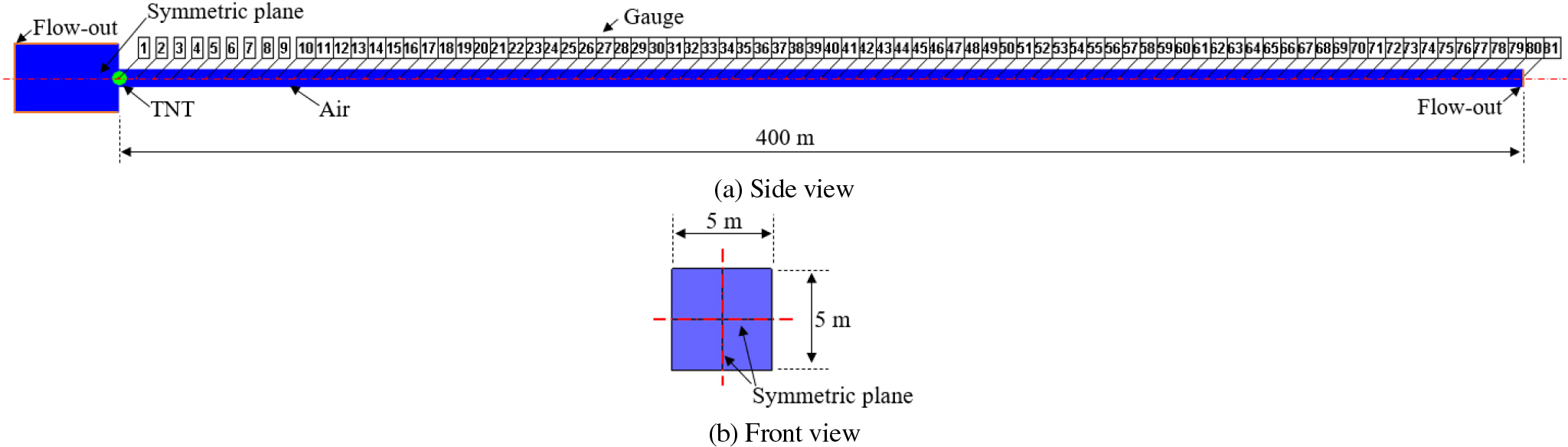
Numerical Investigation of Pressure and Impulse Distributions at Tunnel Portals under Varying Explosive Charge Weights in Long-Span Tunnels
장대형 터널 입구에서 폭약량 변화에 따른 압력 및 충격량 분포 특성에 대한 수치해석
-
Hun Ji, WooSeok Kim
지훈, 김우석
- The present study conducts a numerical analysis of the distribution of blast load propagation inside a long tunnel following a trinitrotoluene (TNT) …
본 연구는 장대형 터널 입구에서 발생한 TNT 폭발로 인해 터널 내부로 전달되는 충격파 하중의 거리별 분포를 수치적으로 분석하였다. 특히 마하파가 평면파로 전이되는 …
- The present study conducts a numerical analysis of the distribution of blast load propagation inside a long tunnel following a trinitrotoluene (TNT) explosion at a portal. This study focuses on the transition of the Mach stem into a planar wave as it enters and on quantifying the attenuation trends of peak pressure and impulse along the interior of the tunnel. A series of numerical simulations were conducted using ANSYS AUTODYN 2023R1, a hydrocode specifically designed for modeling high-explosive blasts. The computational model consists of a straight tunnel with a cross-sectional area of 25m2. Four TNT charge weights of 10, 50, 100, and 500kg were considered, and measurement points were placed along the tunnel centerline to record blast responses at multiple distances. To enable consistent comparisons across different charge weights, the scaled distance parameter Z = D/W was introduced, where D denotes the standoff distance, and W denotes the charge weight. The results indicate that although the absolute values of pressure and impulse vary with charge weight, their normalized responses exhibit a similar attenuation trend with respect to scaled distance. These findings highlight the consistent spatial decay behavior of blast loads under portal explosion conditions and provide useful reference data for evaluating hazard ranges, planning protective measures, and improving blast-resistant tunnel design.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 장대형 터널 입구에서 발생한 TNT 폭발로 인해 터널 내부로 전달되는 충격파 하중의 거리별 분포를 수치적으로 분석하였다. 특히 마하파가 평면파로 전이되는 구간에서 최대 압력 및 충격량의 감쇠 특성을 정량적으로 규명하는 데 중점을 두었다. 해석에는 고폭발물 해석에 특화된 도구인 ANSYS AUTODYN 2023R1을 사용하였으며, 25제곱미터 정사각 단면을 가진 직선형 터널을 대상으로 TNT 중량 10kg, 50kg, 100kg, 500kg 조건을 적용하였다. 터널 중심선 상의 관측 지점을 통해 데이터를 수집하고, 거리(D)를 폭약 중량(W)으로 나눈 환산 거리(Z = D/W)를 도입하여 중량 간 비교를 수행하였다. 분석 결과, TNT 중량에 따라 절대 응답 값은 달랐으나 정규화된 축에서는 최대 압력과 충격량이 유사한 감쇠 경향을 나타냈다. 이러한 결과는 터널 입구부 폭발 시 발생하는 하중 분포가 환산 거리 기준으로 일정한 패턴을 갖는다는 점을 보여주었으며, 향후 방호 설계, 위험 구역 산정 및 폭발 피해 예측 등에 활용 가능한 기초자료를 제공할 수 있을 것으로 기대된다.
-
Numerical Investigation of Pressure and Impulse Distributions at Tunnel Portals under Varying Explosive Charge Weights in Long-Span Tunnels
-
Research Paper
-
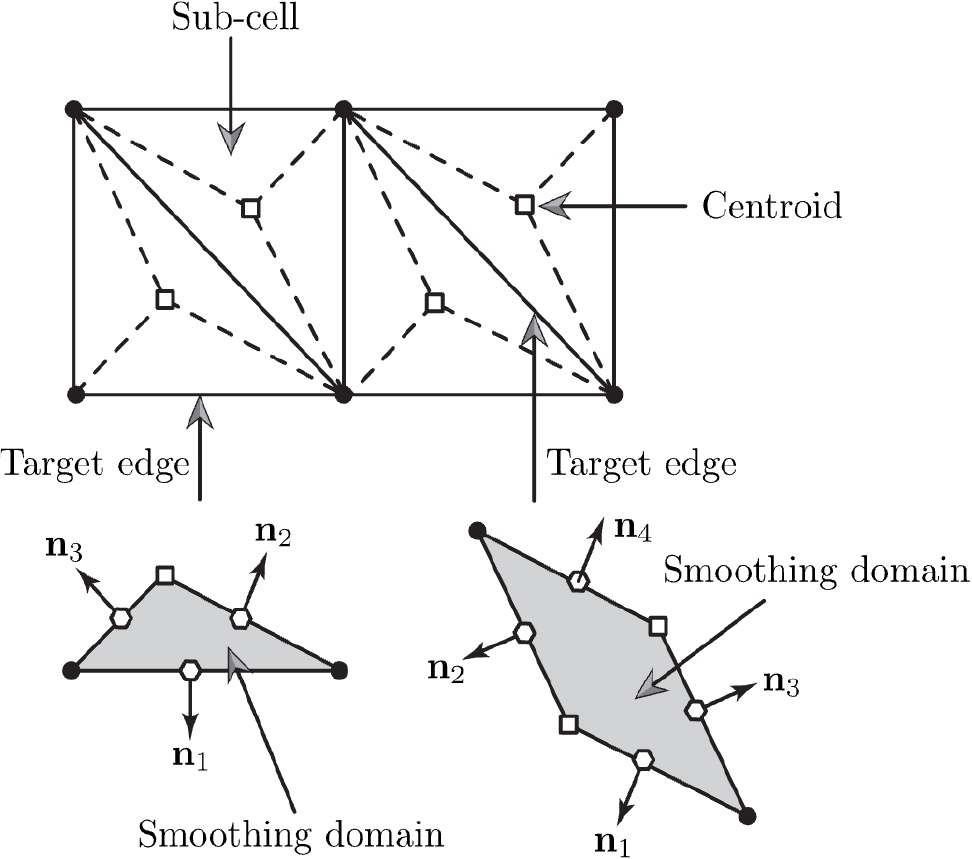
A MATLAB Implementation of ES-FEM-based Topology Optimization
MATLAB으로 구현한 에지 기반 평활화 유한요소법을 도입한 위상 최적화
-
Changkye Lee
이창계
- This paper presents a compact and efficient MATLAB implementation of topology optimization using the edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM). The framework …
본 논문은 에지 기반 평활화 유한요소법(Edge-based smoothed finite element method, ES-FEM)을 도입한 위상 최적화를 간결하고 효율적인 MATLAB 코드로 구현하였다. 제안한 MATLAB 코드는 …
- This paper presents a compact and efficient MATLAB implementation of topology optimization using the edge-based smoothed finite element method (ES-FEM). The framework is designed with pedagogical intent, illustrating how ES-FEM can be effectively vectorized through the systematic construction of smoothing domains around interior and boundary edges, followed by the computation of smoothed stiffness matrices over these domains. Computational efficiency is further enhanced through array preallocation. An improved density filter is incorporated, simplifying the formulation while delivering better performance compared to existing ES-FEM-based topology optimization approaches. With this enhancement, the complete implementation requires only 175 lines of MATLAB code, ensuring both readability and ease of use. Boundary conditions and loading can be customized by modifying only a few lines, making the approach flexible and easily extensible. The full MATLAB code is provided in the Appendix as an accessible starting point for newcomers to topology optimization and ES-FEM, offering a clear and approachable entry point with a gentle learning curve.
- COLLAPSE
본 논문은 에지 기반 평활화 유한요소법(Edge-based smoothed finite element method, ES-FEM)을 도입한 위상 최적화를 간결하고 효율적인 MATLAB 코드로 구현하였다. 제안한 MATLAB 코드는 교육적 목적을 위해 내부 및 경계 에지를 중심으로 평활화 영역을 체계적으로 생성하고, 해당 영역에 대한 평활화 강성 행렬을 계산함으로써 ES-FEM을 효과적으로 벡터화하는 방법을 보여준다. 특히 배열 사전 할당을 통해 계산 효율성을 한층 향상시켰다. 아울러, 개선된 밀도 필터를 도입하여 기존 ES-FEM 기반 위상 최적화 기법보다 수식을 단순화하면서도 계산 성능을 크게 향상시켰다. 이러한 개선으로 전체 MATLAB 코드는 175줄로 구현되어 높은 가독성과 사용 편의성을 갖춘다. 또한 경계 조건과 하중의 적용은 몇 줄만 수정하면 되어, 연구자가 손쉽게 코드를 유연하게 확장할 수 있다. MATLAB 코드는 부록에 수록되어 있으며, 이를 통해 위상 최적화와 ES-FEM에 입문하는 연구자들이 보다 쉽게 학습할 수 있도록 명확하고 직관적인 교육적 자료를 제공하고자 한다.
-
A MATLAB Implementation of ES-FEM-based Topology Optimization
-
Research Paper
-
Joystick Model-based Fragility Analysis of Process Tower Considering Structural Damage
조이스틱 모델 기반 구조 손상을 고려한 증류탑 취약도 분석
-
Se-Hyeok Lee, Euihyun Choi, Sang-ri Yi
이세혁, 최의현, 이상리
- A fault tree-based Bayesian Network methodology has recently been developed to perform the probabilistic safety assessment (PSA) of plant systems under seismic …
지진에 대한 플랜트 시스템의 확률론적 안전성 평가(Probabilistic Safety Assessment, PSA)를 수행하기 위해 고장수목(Fault Tree) 기반의 베이지안 네트워크(Bayesian Network, BN) 방법론이 제안된 바 …
- A fault tree-based Bayesian Network methodology has recently been developed to perform the probabilistic safety assessment (PSA) of plant systems under seismic hazards. Conducting such assessments requires reliable seismic fragility curves for structures and equipment, some of which are provided by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). However, this information is limited in scope and do not adequately represent the wide variety of equipment used in industrial plants. For example, even when redundant facilities are installed to ensure operational continuity of a plant, the same fragility information is often applied uniformly without accounting for the individualized structural conditions. Consequently, the resolution risk assessment outcomes is reduced, limiting informative decision-making. To address this issue, this study selects a distillation tower (one of the key facilities in petrochemical plants) and develops a joystick-type model capable of simulating its damage mechanisms. Three seismic fragility assessment methods, namely multiple stripe analysis (MSA), incremental dynamic analysis (IDA), and cloud analysis, are briefly introduced, and fragility curves are derived for the selected example using each method. The results indicate that the differences among the three methods are relatively small. Furthermore, fragility curves were derived by assuming structural damage scenarios such as anchor rupture. The results confirmed that facility-specific fragility curves are required depending on the structural condition of each facility.
- COLLAPSE
지진에 대한 플랜트 시스템의 확률론적 안전성 평가(Probabilistic Safety Assessment, PSA)를 수행하기 위해 고장수목(Fault Tree) 기반의 베이지안 네트워크(Bayesian Network, BN) 방법론이 제안된 바 있다. 해당 PSA를 수행하기 위해서는 구조물 및 설비들의 지진 취약도 곡선 정보는 필수적이며, 해당 정보는 Federal Emergency Management Agency(FEMA)에서 일부 제공하고 있다. 그러나 다양한 종류의 설비에 비해 제공되는 정보는 매우 제한적이며, 특히 플랜트 운영지속성을 위해 여분의 설비가 배치된 경우에도 개별 설비의 구조적 상태가 반영되지 못하고 같은 정보가 사용되어, 결과적으로 일률적인 리스크 평가와 제한적인 의사결정만이 이루어질 수 있음을 확인하였다. 따라서 본 연구에서는 플랜트의 여러 주요 설비 중 석유화학 플랜트의 증류탑을 선정하고, 증류탑의 손상 메커니즘을 모사 가능한 조이스틱 모델을 구축하였다. 이와 더불어 지진 취약도 해석 기법 세가지(다중띠해석, 증분독적해석, 산점도분석법)에 대해 간략히 설명하고 주어진 예제에 대해 각 기법을 이용하여 취약도 곡선을 도출하였다. 도출된 결과에서 세기법의 차이가 크지 않음을 확인하였고, 앵커 파단과 같은 구조적 손상 시나리오를 가정하여 취약도를 도출하였는데, 이 결과를 토대로 개별 설비의 구조적 상태에 따라 상이한 취약도 곡선이 필요함을 확인할 수 있었다.
-
Joystick Model-based Fragility Analysis of Process Tower Considering Structural Damage
-
Research Paper
-
Pushover Analysis and Partially Scaled Model Test Verification for Evaluating the Wind-Resistant Performance of an Existing 154kV Transmission Tower
기설 154kV 송전철탑의 내풍성능 평가를 위한 Pushover 해석 및 부분축소모형 실험 검증
-
Gil-Young Chung, Gi-Bae Kim, Hyung-Kui Park, Soo-Hyuk Chang
정길영, 김기배, 박형규, 장수혁
- This study evaluated the structural performance of a 154kV straight-type transmission tower susceptible to strong winds. Previous studies have shown that transmission …
본 연구는 강풍에 취약한 설비로 선정된 154kV 직선형 송전철탑을 대상으로 극한 풍하중에 대한 구조 성능을 검토하였다. 선행연구에 따르면 송전철탑은 정면풍보다 45° 풍향에서 …
- This study evaluated the structural performance of a 154kV straight-type transmission tower susceptible to strong winds. Previous studies have shown that transmission towers are more vulnerable under 45° wind than under frontal wind, and this condition was considered in the analysis. A pushover analysis of the full-scale tower was conducted using ABAQUS to identify critical members under extreme wind. Based on the results, a half-scale model with bearing- and friction-type bolted connections was fabricated. Two actuators were used to reproduce the horizontal forces and bending moments from the full-scale analysis in accordance with similarity laws. Tests showed that increasing bolt pretension reduced the yield displacement by about 30%, while the yield load remained nearly unchanged. For friction-type connections, differences in yield load and displacement between analysis and experiment were within 5%, confirming the reliability of the pushover analysis. Future work will propose reinforcement strategies for critical members and verify their effectiveness through scaled-model tests to improve wind and seismic resistance.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구는 강풍에 취약한 설비로 선정된 154kV 직선형 송전철탑을 대상으로 극한 풍하중에 대한 구조 성능을 검토하였다. 선행연구에 따르면 송전철탑은 정면풍보다 45° 풍향에서 더 취약한 거동을 보이며, 이를 고려하여 ABAQUS를 이용한 Pushover 해석을 수행하였다. 극한 풍속 조건에서의 취약 부재와 거동 특성을 분석한 후, 길이 차원에서 1/2 상사율을 적용한 부분축소모형을 제작하였으며, 지압이음 조건과 마찰이음 조건으로 구분하였다. 또한 두 대의 가력기를 이용해 전체모델에서 산정된 수평력과 휨모멘트를 상사법칙에 따라 재현하였다. 실험 결과, 볼트 체결력을 향상시킨 경우 항복변위는 약 30% 감소했으나 항복하중에는 큰 차이가 없었다. 특히 마찰이음 조건에서는 해석과 실험의 항복하중 및 항복변위가 모두 5% 이내의 오차를 보여 Pushover 해석의 신뢰성이 검증되었다. 향후 연구에서는 주요 부재의 보강 방안을 수립하고, 보강된 부분축소모형 실험을 통해 내풍 및 내진 성능 향상을 검증할 예정이다.
-
Pushover Analysis and Partially Scaled Model Test Verification for Evaluating the Wind-Resistant Performance of an Existing 154kV Transmission Tower
-
Research Paper
-
Analysis of the Material Properties of Lightweight Air-Entrained Concrete using Seashell Aggregates
해양패각 잔골재를 활용한 경량 AE 콘크리트의 특성 분석
-
Ye-Rim Kim, Bongsik Kim, Yongsoo Ji, Sang-Yeop Chung
김예림, 김봉식, 지용수, 정상엽
- Concrete is the most widely consumed construction material in the world, and its main component—ordinary Portland cement (OPC)—accounts for about 8% of …
콘크리트는 세계에서 가장 많이 사용되는 건설재료이며, 그 주요 구성요소인 보통 포틀랜드 시멘트(OPC)는 전 세계 CO2 배출량의 약 8%를 차지한다. 또한 콘크리트 …
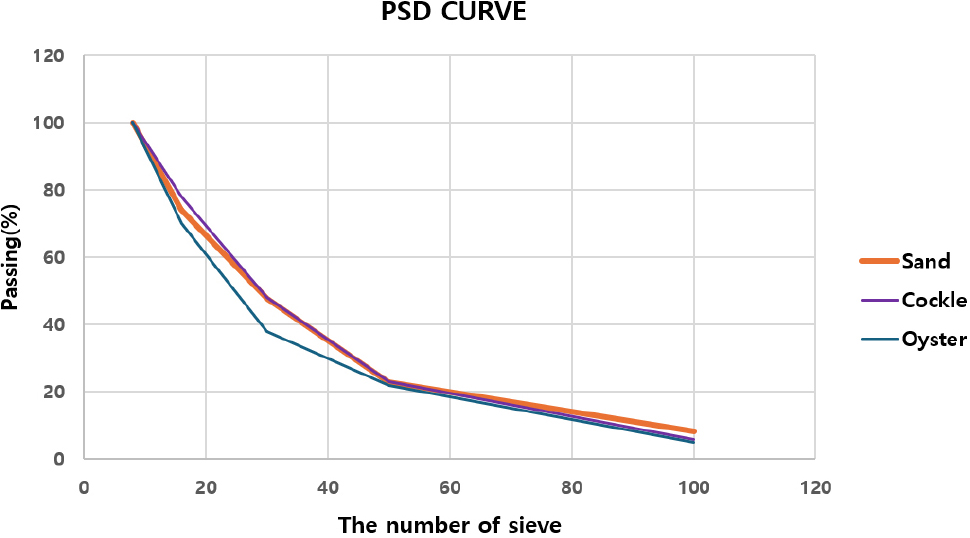
- Concrete is the most widely consumed construction material in the world, and its main component—ordinary Portland cement (OPC)—accounts for about 8% of global CO2 emissions. Furthermore, the rising demand for concrete necessitates the extraction of larger amounts of sand and coarse aggregates, posing environmental concerns. Consequently, efforts to develop functional construction materials and utilize alternative aggregates have been intensified. As such, seashells have gained attention for their abundant calcium carbonate content. Furthermore, among many functional construction materials, foamed concrete has emerged as eco-friendly and energy-efficient material, characterized by superior insulation performance, low density, and frost-resistance owing to its numerous internal pores. In addition, its porous nature also enables effective noise reduction, highlighting its potential for soundproofing applications. Considering these advantages, this study investigates foamed concrete incorporating seashell aggregates as a sustainable solution to natural sand depletion and marine environmental pollution. A post-foaming method was employed, and an air-entraining (AE) agent was used as the foaming agent to entrain air in the concrete. Cockle and oyster shells were used as alternatives to conventional sand aggregates. Samples were produced by varying seashells replacement ratios and AE agent contents. Subsequently, their micro-structural characteristics were investigated and correlated with the corresponding mechanical properties. Furthermore, the sound absorption performance of foamed concrete incorporating seashells was evaluated using numerical approaches. The findings show that incorporating seashells can enhance the performance of foamed concrete without compromising its mechanical performance.
- COLLAPSE
콘크리트는 세계에서 가장 많이 사용되는 건설재료이며, 그 주요 구성요소인 보통 포틀랜드 시멘트(OPC)는 전 세계 CO2 배출량의 약 8%를 차지한다. 또한 콘크리트 수요 증가로 인해 막대한 양의 모래와 굵은 골재 생산이 요구되면서 환경 생태계 파괴 문제가 증가하고 있다. 이에 따라 기능성 건설재료 개발과 대체 골재 활용에 대한 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있으며, 특히 해양 패각은 풍부한 탄산칼슘 함량으로 주목받고 있다. 한편, 다수의 내부 기공을 가지는 기포콘크리트는 우수한 단열 성능, 낮은 밀도, 내동해성을 특징으로 하는 친환경・에너지 효율적 재료로 떠오르고 있다. 게다가, 기포콘크리트는 기공 특성으로 인한 소음 저감 성능이 우수하여 차음・흡음 건설재료로의 적용 가능성을 지닌다. 본 연구에서는 이러한 장점을 결합하여, 해양 패각을 혼입한 기포콘크리트를 대상으로 천연 잔골재 고갈 문제와 해양 환경오염 문제를 동시에 해결하고자 하였다. 연구 수행을 위해 post-foaming 공법을 적용하고, 공기연행제(AE제)를 발포제로 사용하여 공극을 형성하였으며, 꼬막 및 굴 패각을 모래 잔골재 대체재로 활용하였다. 다양한 패각 대체율과 AE제 함량 조건에서 제작된 시편에 대해 미세구조 특성을 분석하고, 기계적 성능과의 상관관계를 분석하였단. 또한 수치해석 기법을 통해 패각 혼입 기포콘크리트의 흡음 성능을 평가하였다. 본 연구는 해양 패각을 혼입한 기포콘크리트에서 기계적 성능을 저하시키지 않으면서 흡음 및 단열과 같은 기능적 성능 향상이 가능함을 확인하였다.
-
Analysis of the Material Properties of Lightweight Air-Entrained Concrete using Seashell Aggregates
-
Research Paper
-
Bayesian Optimization Design for Minimizing Gear Transmission Error
기어 전달오차 최소화를 위한 베이지안 최적화 설계
-
Jeong-Min Park, Ki-Hyeok Bae, Min-Seo Kang, Bonyoung Koo, Min-Geun Kim
박정민, 배기혁, 강민서, 구본용, 김민근
- This paper proposes an optimal design method for minimizing gear transmission error using Bayesian Optimization to reduce gear noise and vibration. Transmission …
본 논문에서는 기어 소음 및 진동 저감을 위해 베이지안 최적화 기법을 이용하여 기어 전달오차를 최소화하는 최적설계 기법을 제안하였다. 이는 기어의 형상에 큰 …
- This paper proposes an optimal design method for minimizing gear transmission error using Bayesian Optimization to reduce gear noise and vibration. Transmission error is significantly influenced by gear geometry. Conventional ISO 6336 and AGMA 2101 analyses cannot fully reflect the actual tooth shape or contact ratio, while finite element analysis provides high accuracy but entails substantial computational cost due to fine meshing and nonlinear contact conditions. In this study, a simplified finite element model considering contact ratio was developed to improve computational efficiency. A Gaussian process surrogate model was constructed to predict transmission error using a limited number of samples, and the expected improvement criterion was employed to efficiently search for new optimal points. The effectiveness of the proposed optimization framework was verified by comparing its results with those obtained from a genetic algorithm, demonstrating that the Bayesian Optimization approach can achieve high accuracy with reduced computational effort.
- COLLAPSE
본 논문에서는 기어 소음 및 진동 저감을 위해 베이지안 최적화 기법을 이용하여 기어 전달오차를 최소화하는 최적설계 기법을 제안하였다. 이는 기어의 형상에 큰 영향을 받는다. 기존의 ISO 6336과 AGMA 2101 기반의 전달오차 해석은 기어 형상과 물림률을 충분히 반영하지 못하며, 유한요소해석은 정확도가 높으나 세밀한 요소망과 접촉 비선형 해석으로 인해 계산 비용이 매우 크다는 한계가 있다. 본 연구에서는 물림률을 고려한 유한요소 간소화모델을 구성하여 비교적 적은 샘플로 정확한 확률 모델을 만들 수 있는 가우시안 프로세스 기반 대리모델과, 여기서 얻어진 기대치 개선값을 바탕으로 새로운 최적점을 탐색하였다. 제안된 기법의 결과를 유전자 알고리즘 기법과 비교하여 유효성을 검증하였다.
-
Bayesian Optimization Design for Minimizing Gear Transmission Error
-
Research Paper
-
Modal and Dynamic Analysis of a Counter-Rotating Propeller Shaft System
상반회전 프로펠러 축계의 고유진동과 동적 해석
-
Jaehyun Kim
김재현
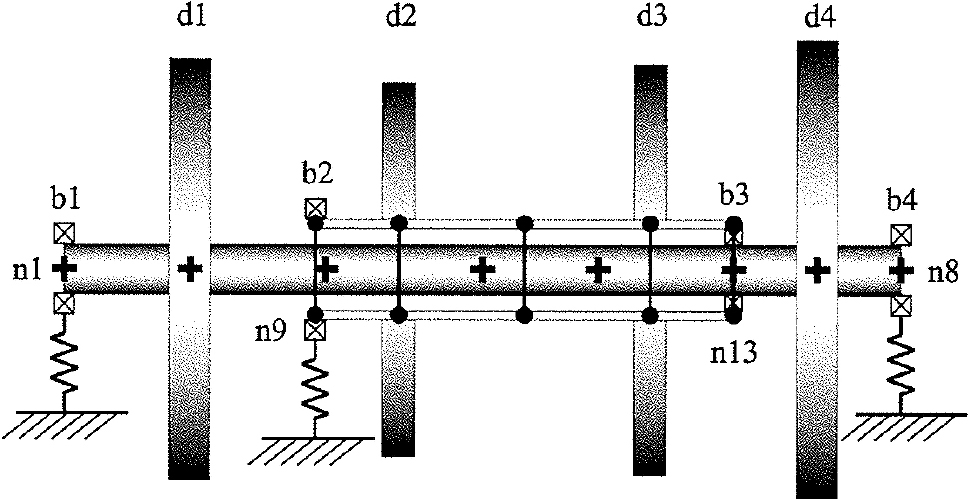
- This study proposes a numerical analysis method for evaluating the dynamic characteristics of a counter-rotating propeller (CRP) dual shaft system. The developed …
본 논문에서는 상반회전 추진 프로펠러 이중축계의 회전 동특성을 정밀하게 분석하기 위한 수치해석 방법을 제안하였다. 제안된 해석 기법은 티모쉔코 보 이론 기반의 유한요소법을 …
- This study proposes a numerical analysis method for evaluating the dynamic characteristics of a counter-rotating propeller (CRP) dual shaft system. The developed method employs a finite element formulation based on Timoshenko beam theory, incorporating gyroscopic coupling and bearing damping effects to derive the governing equations of motion. The proposed in-house computational code was verified through comparison with a reference co-axial rotor model, demonstrating excellent agreement in both natural frequencies and Campbell diagram trends, thereby validating the accuracy of the formulation. A parametric investigation revealed that increasing the inter-shaft bearing stiffness effectively rises the natural frequencies, thereby avoiding critical resonances within the operational speed range, whereas the influence of shaft diameter was relatively minor. The proposed numerical approach offers a reliable and efficient analytical tool for the design evaluation and vibration stability assessment of CRP dual shaft propulsion systems. Future work will focus on extending the model to account for nonlinear bearing characteristics and fluid–structure interaction effects to enhance its predictive capability under practical operating conditions.
- COLLAPSE
본 논문에서는 상반회전 추진 프로펠러 이중축계의 회전 동특성을 정밀하게 분석하기 위한 수치해석 방법을 제안하였다. 제안된 해석 기법은 티모쉔코 보 이론 기반의 유한요소법을 이용하여 자이로스코픽 효과와 베어링 감쇠를 포함한 운동방정식을 정식화하였다. 개발된 해석 코드는 기존 동축 회전체 모델과의 비교를 통해 검증되었으며, 고유진동수와 캠벨선도 결과가 매우 잘 일치함을 확인하였다. CRP 축계의 시뮬레이션 결과 1차 공진모드에서 내축의 변위가 외축보다 커 축간 충돌 가능성이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 베어링 강성 증가 시 고유진동수가 상승하여 공진영역을 회피할 수 있었으며, 축 직경 변화는 상대적으로 영향이 작았다. 제안된 해석 기법은 상반회전 추진 이중축계의 설계 평가 및 진동 안정성 분석에 유용하게 활용될 수 있으며, 향후에는 비선형 베어링 특성 및 유체–구조 연성효과를 포함한 확장 연구로 발전시킬 수 있을 것이다.
-
Modal and Dynamic Analysis of a Counter-Rotating Propeller Shaft System
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea
Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea
Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea











