-
Research Paper
-
Development of a Two-Dimensional Numerical Model for Dynamic Analysis of Vertical Breakwaters Subjected to Impulsive Water Wave Loads
충격쇄파에 대한 직립식 방파제의 2차원 동적 해석을 위한 해석모델 구축
-
Hyeok-Ju Lee, Jong-In Lee, Jae-Min Kim
이혁주, 이종인, 김재민
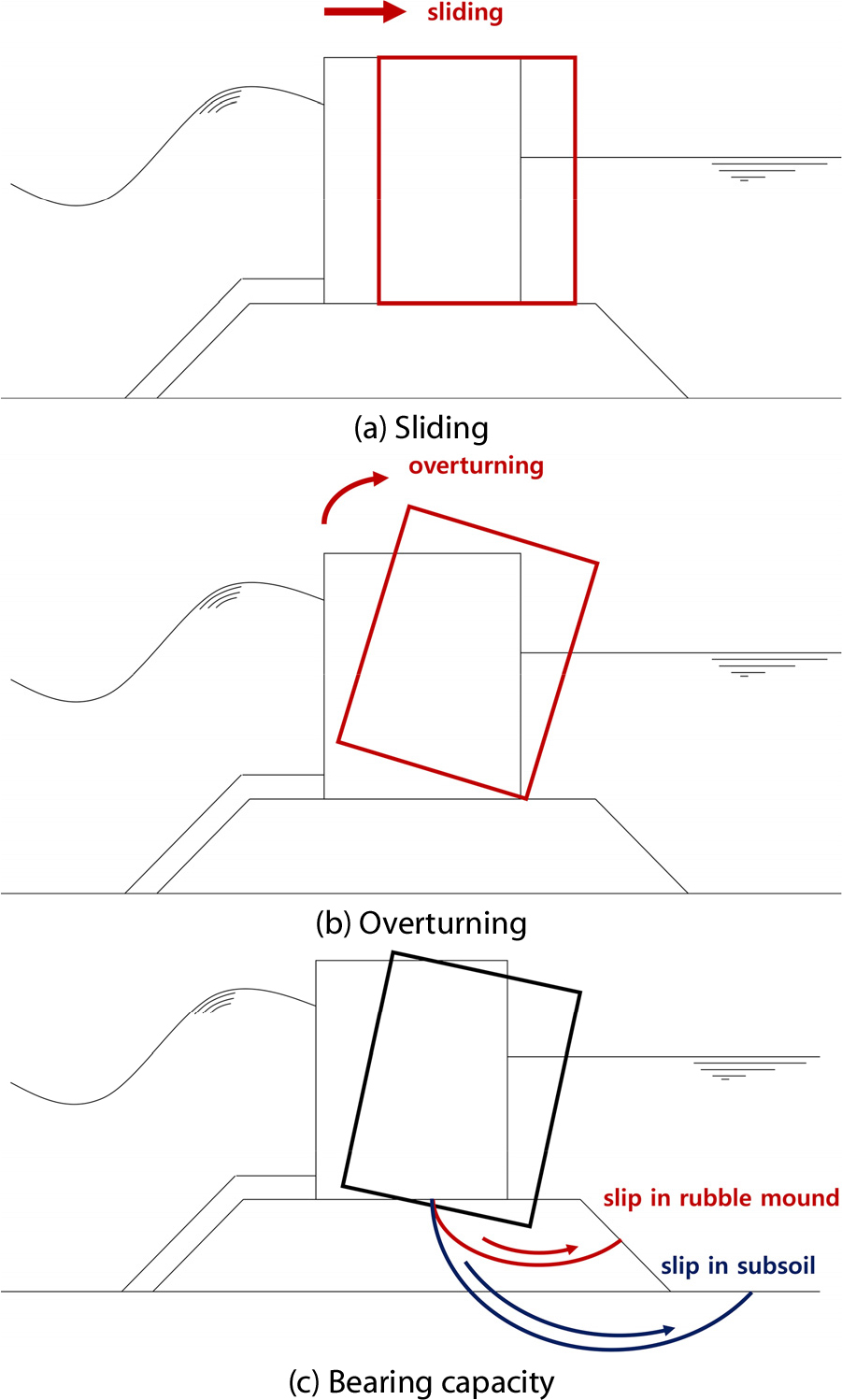
- This study develops a two-dimensional finite element model to accurately analyze the dynamic behavior of vertical breakwaters subjected to impulsive water wave …
이 연구는 충격쇄파 하중에 대한 직립식 방파제의 동적 거동을 정밀히 분석하기 위해 유한요소 기반의 2차원 해석 모델을 구축하였다. 기존의 단순화된 해석 방법이 …
- This study develops a two-dimensional finite element model to accurately analyze the dynamic behavior of vertical breakwaters subjected to impulsive water wave loads. To overcome the limitations of simplified analytical approaches, a refined numerical model is constructed by incorporating fluid elements, a nonlinear soil model, contact nonlinearity, and perfectly matched layers (PMLs). Additionally, the time history of impulsive water wave loads is modeled based on theoretical wave pressure equations to evaluate the sliding displacement of the breakwater. The numerical results indicate that the nonlinear soil model induces significantly larger sliding displacements than the elastic soil model. Furthermore, the application of PMLs significantly enhances the numerical stability and accuracy of the analysis when compared with conventional fixed boundary conditions. The proposed modeling approach contributes to the development of accurate dynamic analysis techniques for the design and safety assessment of vertical breakwaters and provides a foundation for predicting their structural performance under extreme wave conditions.
- COLLAPSE
이 연구는 충격쇄파 하중에 대한 직립식 방파제의 동적 거동을 정밀히 분석하기 위해 유한요소 기반의 2차원 해석 모델을 구축하였다. 기존의 단순화된 해석 방법이 지닌 한계를 극복하고자, 유체 요소, 비선형 지반 모델, 접촉 비선형성, 에너지흡수경계요소를 포함한 정밀한 2차원 수치해석 모델을 구축하였다. 또한, 이론적 파압 공식을 기반으로 충격쇄파 하중의 시간이력을 모델링하여 방파제의 활동량을 평가하였다. 해석 결과, 비선형 지반 모델은 탄성 지반 대비 더 큰 활동량을 유발하는 것으로 나타났으며, PML(Perfectly Matched Layer)은 고정 경계 조건과 비교했을 때 해석 안정성과 정확성을 크게 향상시키는 것으로 나타났다. 이 연구는 직립식 방파제 설계 및 안전성 평가를 위한 정밀 동적 해석 기술 개발에 기여하며, 극한 조건에서도 방파제 성능을 예측할 수 있는 기반을 제공할 것으로 기대된다.
-
Development of a Two-Dimensional Numerical Model for Dynamic Analysis of Vertical Breakwaters Subjected to Impulsive Water Wave Loads
-
Research Paper
-
Slip Failure Analysis and Evaluation of Wave Pressure Effects on Rubble Mound Breakwater using the Strength Reduction Method
강도감소법을 이용한 경사식 방파제의 슬립 파괴 해석 및 파압 영향 평가
-
Hyeok-Ju Lee, Jong-In Lee, Jae-Min Kim
이혁주, 이종인, 김재민
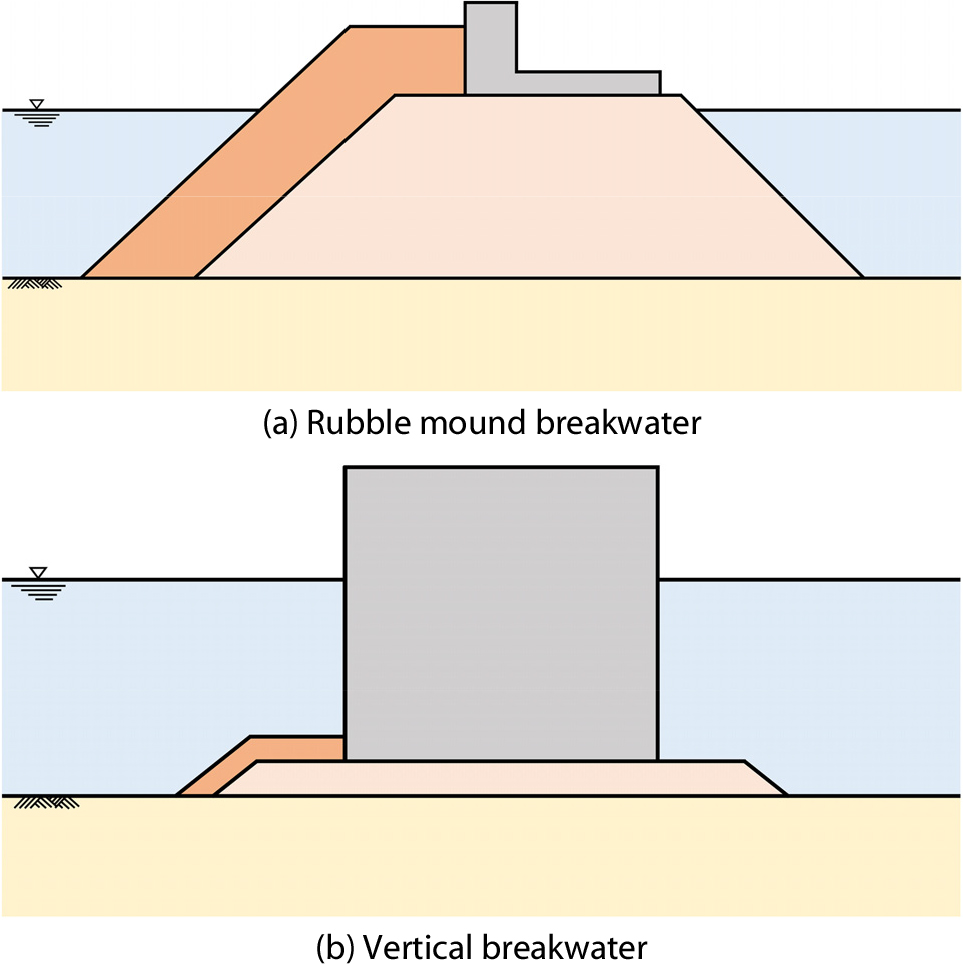
- This study performed a slip failure analysis and evaluated the structural stability of a rubble mound breakwater under wave pressure using the …
이 연구에서는 파랑 하중을 받는 경사식 방파제의 구조적 안정성을 평가하기 위하여 강도감소법(Strength Reduction Method)을 이용한 슬립 파괴 해석을 수행하였다. 강도감소법의 신뢰성은 기존의 …
- This study performed a slip failure analysis and evaluated the structural stability of a rubble mound breakwater under wave pressure using the strength reduction method (SRM). The reliability of the SRM was verified by reproducing the results of a conventional slope stability analysis using ABAQUS finite element analysis. Considering the wave pressure distribution acting on the crown wall, the slip failure behavior within the rubble mound was analyzed. The analysis results showed that, under the sectional configuration and material properties adopted in this study, a non-circular slip failure surface was formed at a wave height of 7m, and the factor of safety was estimated to be approximately 1.68. In addition, uncertainty analysis using the Latin hypercube sampling was conducted to derive the fragility curve of the rubble mound breakwater with respect to variations in wave height. The results demonstrated that the probability of failure increased rapidly with wave height, and the critical wave height was evaluated to be approximately 6.85m. This study demonstrates the effective applicability of numerical analysis based on SRM to the wave-resisting stability and fragility evaluation of rubble mound breakwaters.
- COLLAPSE
이 연구에서는 파랑 하중을 받는 경사식 방파제의 구조적 안정성을 평가하기 위하여 강도감소법(Strength Reduction Method)을 이용한 슬립 파괴 해석을 수행하였다. 강도감소법의 신뢰성은 기존의 사면 안정 해석 결과를 유한요소해석 프로그램인 ABAQUS로 재현함으로써 검증하였다. 또한, 상치 콘크리트에 작용하는 파압 분포를 고려하여 경사식 방파제 내부의 슬립 파괴 거동을 분석하였다. 해석 결과, 이 연구에서 사용한 단면 형상 및 물성 조건 하에서 파고 7m 조건에서 비원형 슬립 파괴면이 발생하였고, 안전율은 약 1.68로 산정되었다. 추가적으로 Latin Hypercube Sampling을 이용한 불확실성 해석을 수행하여 파고 변화에 따른 경사식 방파제의 취약도 곡선을 도출하였다. 분석 결과 파고가 증가함에 따라 파괴 확률이 급격히 증가하였으며, 임계 파고는 약 6.85m로 평가되었다. 이 연구는 강도감소법 기반 수치해석이 경사식 방파제의 내파 안정성 및 취약도 평가에 효과적으로 적용될 수 있음을 보여준다.
-
Slip Failure Analysis and Evaluation of Wave Pressure Effects on Rubble Mound Breakwater using the Strength Reduction Method
-
Research Paper
-
Nonlinear Seismic Response Analysis of Cylindrical Liquid Storage Tanks on Flexible Soil Considering Base Uplift
유연한 지반에 놓인 원통형 액체저장탱크의 바닥 들림을 고려한 비선형 지진응답해석
-
Lee Jin Ho, Dong Sop Rhee, Jeong-Rae Cho
이진호, 이동섭, 조정래
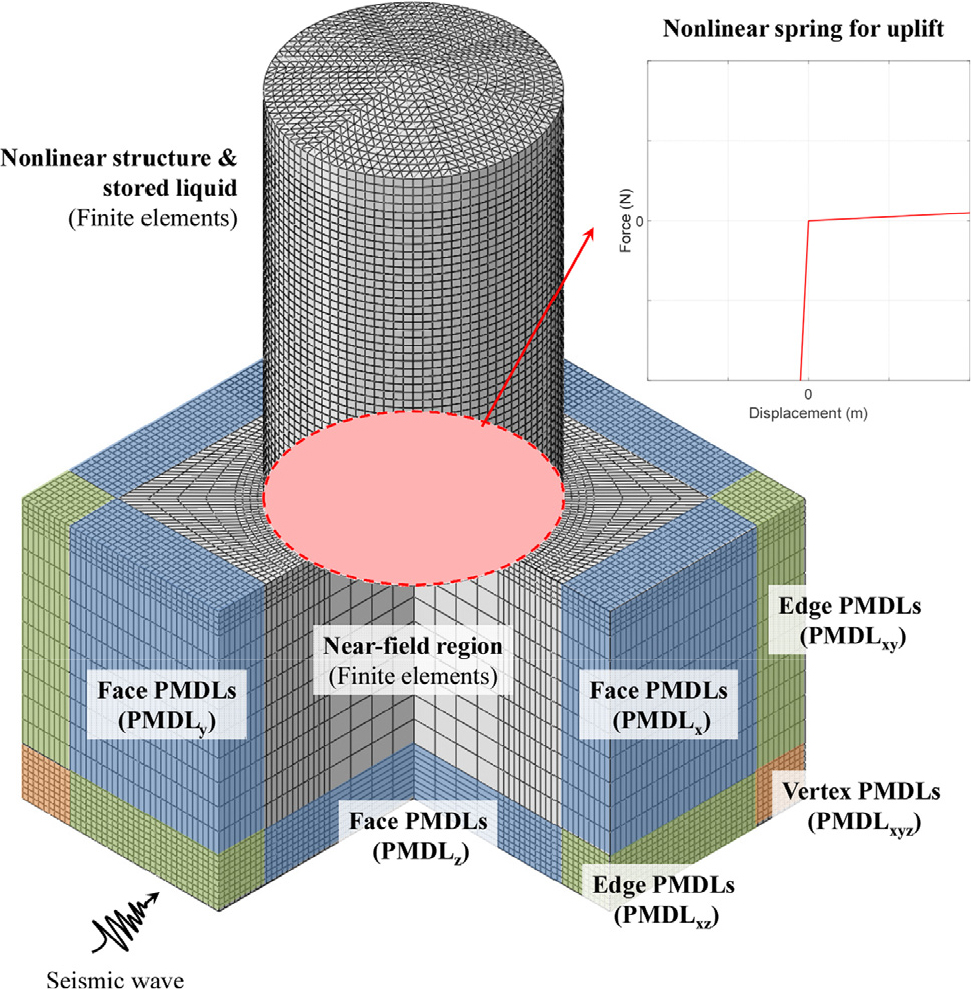
- This study develops a finite element analysis framework to rigorously evaluate the nonlinear seismic response of unanchored cylindrical liquid storage tanks resting …
유연한 지반 위에 놓인 비정착식 원통형 액체저장탱크의 지진응답을 바닥판의 들림을 고려하여 산정하기 위한 유한요소 해석기법을 개발한다. 지반-구조물 상호작용력과 저장 액체 동수압력을 재료 …
- This study develops a finite element analysis framework to rigorously evaluate the nonlinear seismic response of unanchored cylindrical liquid storage tanks resting on flexible soil, with explicit consideration of base uplift. Soil-structure interaction forces, including energy radiation into the infinite soil domain, and hydrodynamic forces generated by the stored liquid are coupled within a nonlinear finite element model of the tank, accounting for both material and geometric nonlinearities. Base uplift is simulated using nonlinear spring elements with negligible tensile stiffness. The proposed model is employed to accurately compute the seismic response of liquid storage tanks subjected to earthquake ground motion. The results indicate that consideration of material and geometric nonlinearities significantly increases stresses in the tank wall, resulting in enhanced plastic response. However, when base uplift is included, the base plate is allowed to uplift freely, which reduces structural stresses and plastic deformation. These findings demonstrate that accurate seismic response evaluation of fluid-structure-soil interaction systems that are not fully anchored to the ground requires rigorous consideration of boundary nonlinearities, such as separation at the soil-structure contact interface, in addition to material and geometric nonlinear behavior.
- COLLAPSE
유연한 지반 위에 놓인 비정착식 원통형 액체저장탱크의 지진응답을 바닥판의 들림을 고려하여 산정하기 위한 유한요소 해석기법을 개발한다. 지반-구조물 상호작용력과 저장 액체 동수압력을 재료 및 기하 비선형 거동을 고려한 구조물의 비선형 유한요소 모형과 결합한다. 구조물과 지반 사이의 들림을 모사하기 위해 인장에 대해서는 강성을 무시할 수 있는 비선형 스프링 요소를 사용한다. 개발된 비선형 유한요소 모델을 사용하여 지진지반운동이 작용하는 액체저장탱크의 지진응답을 정밀히 산정한다. 구조물의 재료 및 기하 비선형 거동을 고려하면 구조물 벽체의 응력이 크게 증가하여 소성 응답이 증가하지만, 바닥 들림까지 고려하게 되면 구조물 바닥이 자유롭게 들리게 됨으로써 구조물의 응력과 소성 응답이 크게 감소하게 된다. 그러므로 구조물의 재료 및 기하 비선형 거동 뿐만이 아니라 구조물과 지반 접촉면의 분리(바닥 들림)와 같은 경계 비선형 거동을 엄밀히 고려하여 비정착 유체-구조물-지반 상호작용계의 지진응답을 정확히 산정해야 할 것이다.
-
Nonlinear Seismic Response Analysis of Cylindrical Liquid Storage Tanks on Flexible Soil Considering Base Uplift
-
Research Paper
-
A Study on the Buckling Resistance of Large-Diameter Suction Anchors for Mooring Systems
계류용 대구경 석션앵커의 좌굴성능에 대한 연구
-
Kwan Young Hong, Dae Jin Jung, GyeHee Lee
홍관영, 정대진, 이계희
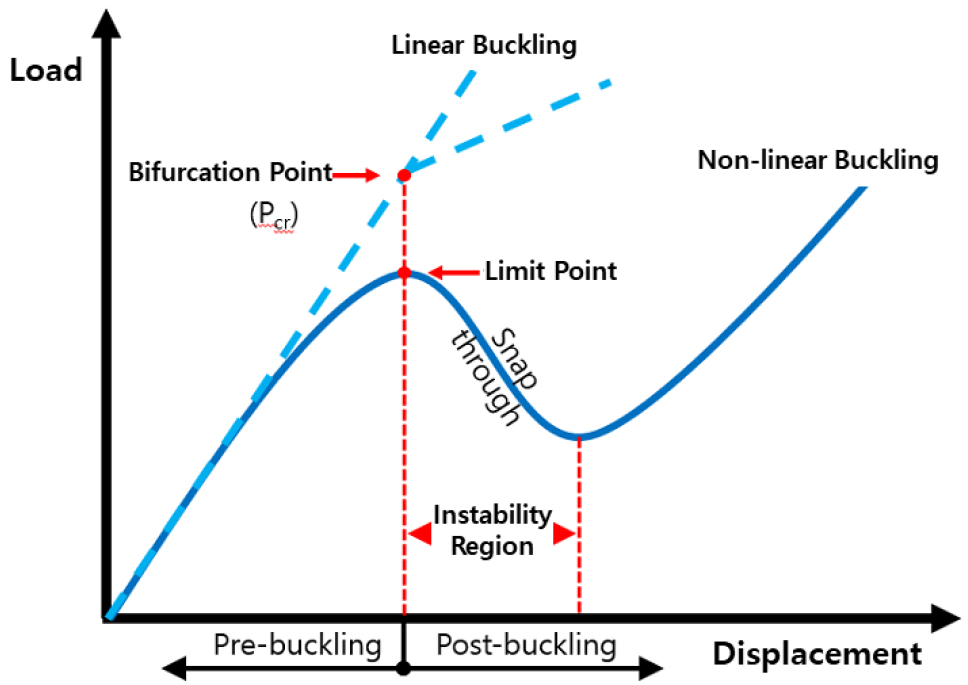
- This study conducts a non-linear buckling analysis on mooring suction anchors using the finite element method (FEM) to evaluate their buckling behavior. …
본 연구에서는 계류용 석션앵커에 대해서 유한요소법을 이용한 비선형 좌굴해석을 수행하여 좌굴거동을 산정하고 이를 석션앵커의 좌굴설계에 주로 적용되고 있는 설계기준에서 제시하고 있는 좌굴거동과 …
- This study conducts a non-linear buckling analysis on mooring suction anchors using the finite element method (FEM) to evaluate their buckling behavior. The results were compared and analyzed against the values in current design codes commonly applied to the buckling design of suction anchors. The numerical model was constructed using shell elements to appropriately capture the buckling modes. The analysis evaluated both the simplified loading conditions used in design codes and the complex combined loading states of suction anchors installed in subsea environments. The results indicated that for suction anchors, out-of-plane loads are more dominant than in-plane axial loads. While the Det Norske Veritas (DNV) design code, which covers out-of-plane loading conditions, appeared to demonstrate higher applicability, an accurate evaluation of buckling behavior using FEA is necessary for cases involving torsion, shear force, and hydrostatic out-of-plane loads. Additionally, further research is required for the estimation of buckling strength and safety factors to ensure consistent safety levels when performing buckling evaluations based on both design codes and numerical analysis.
- COLLAPSE
본 연구에서는 계류용 석션앵커에 대해서 유한요소법을 이용한 비선형 좌굴해석을 수행하여 좌굴거동을 산정하고 이를 석션앵커의 좌굴설계에 주로 적용되고 있는 설계기준에서 제시하고 있는 좌굴거동과 비교 분석하였다. 해석모델은 shell요소를 이용하여 좌굴형상이 적절히 반영되도록 구성하였으며 설계기준에서 사용되는 단순화된 하중조건과 해중에서 설치되는 석션앵커의 복합적인 하중상태를 각각 고려하여 해석을 수행하였다. 그 결과 석션앵커의 좌굴거동은 면외방향 하중이 면내 수직하중보다 지배적이고, 면외방향 하중조건을 명시하고 있는 DNV설계기준이 보다 적용성이 높아 보이지만 비틀림과 전단력, 수리정역학적 면외하중의 경우에는 유한요소해석을 이용한 정확한 좌굴거동평가가 필요할 것으로 판단되었다. 추가적으로 설계기준과 해석에 의한 좌굴평가시 일관된 안전성을 확보할 수 있는 좌굴강도와 안전계수의 산정에 대한 연구가 필요할 것으로 판단된다.
-
A Study on the Buckling Resistance of Large-Diameter Suction Anchors for Mooring Systems
-
Research Paper
-
Design of Three-Dimensional Functionally Graded Composite Structures to Maximize Stiffness and Natural Frequency
강성과 고유진동수 최대화를 위한 3차원 경사기능 복합재 구조 설계
-
Hak-Yong Jang, Jeonghoon Yoo
장학용, 유정훈
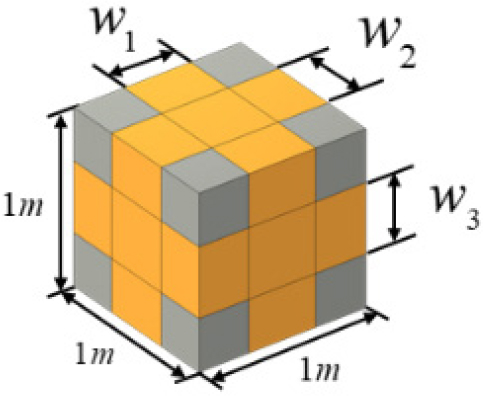
- This study proposes a design methodology for three-dimensional functionally graded composite structures (FGCSs) by integrating the concept of functionally graded materials (FGMs) …
본 논문에서는 경사기능재료(Functionally Graded Material, FGM) 개념과 위상최적설계 방법을 통해 3차원 경사기능복합재 구조(Functionally Graded Composite Structure, FGCS)의 설계 방법을 제안한다. 다중 스케일 …
- This study proposes a design methodology for three-dimensional functionally graded composite structures (FGCSs) by integrating the concept of functionally graded materials (FGMs) with a topology optimization framework. For the design of multiscale composite structures, anisotropic material properties are evaluated using a representative volume element (RVE)–based machine learning module, combined with rotation matrix calculations based on unit quaternions. In addition, a multi-objective optimization is performed with structural stiffness and natural frequency as objective functions to evaluate the optimized structural configurations and their performance under diverse physical environments. The proposed approach enables systematic design of FGCSs with enhanced stiffness and dynamic characteristics.
- COLLAPSE
본 논문에서는 경사기능재료(Functionally Graded Material, FGM) 개념과 위상최적설계 방법을 통해 3차원 경사기능복합재 구조(Functionally Graded Composite Structure, FGCS)의 설계 방법을 제안한다. 다중 스케일 복합재 구조 설계 시 이방성 재료 물성치의 계산은 RVE 기반 ML 모듈과 단위 사원수를 활용한 회전 행렬 계산을 통해 수행된다. 또한, 본 연구에서는 다양한 물리적 환경을 설계에 반영하기 위해 구조물의 강성과 함께 고유진동수를 목적함수로 설정한 다중 목적함수 최적설계를 수행하여 구조물의 최적화 형상과 성능을 분석한다.
-
Design of Three-Dimensional Functionally Graded Composite Structures to Maximize Stiffness and Natural Frequency
-
Research Paper
-
Performance Evaluation of Variable Stiffness Vibration Control for a Single-Degree-of-Freedom System Using DDPG Reinforcement Learning
DDPG 강화학습을 이용한 단자유도 진동계의 가변강성 진동제어 성능평가
-
Wonsuk Park
박원석
- This study aims to clarify the performance characteristics and limitations of reinforcement learning (RL)-based controllers for structural vibration control through an objective …
이 논문에서는 강화학습 기반 제어기와 전통적인 제어기를 동일한 조건에서 비교함으로써 구조 진동 제어 문제에서 강화학습 제어기의 성능 특성과 한계를 규명하는 것을 목적으로 …
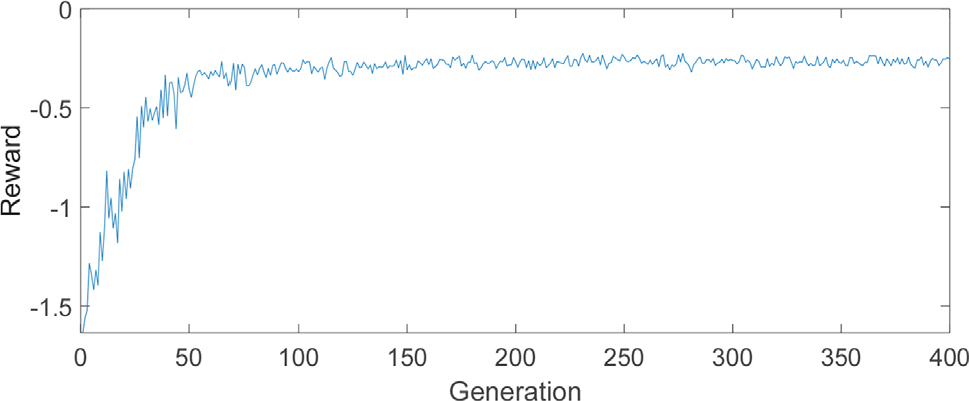
- This study aims to clarify the performance characteristics and limitations of reinforcement learning (RL)-based controllers for structural vibration control through an objective comparison with conventional control methods under identical conditions. A single-degree-of-freedom variable stiffness system is considered, and an RL-based controller is designed using the deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithm. Its performance is compared with that of bang-bang control and clipped-optimal control. Numerical simulations are conducted for both free vibration and forced vibration under the El Centro earthquake ground acceleration, and the nominal performance and robustness against sensor noise are evaluated. The results show that the DDPG-based controller exhibits competitive robustness in free vibration control but does not consistently outperform conventional controllers in forced vibration control. These findings offer fundamental insights into the practical capabilities and inherent limitations of RL-based vibration control under equivalent objective functions and system conditions.
- COLLAPSE
이 논문에서는 강화학습 기반 제어기와 전통적인 제어기를 동일한 조건에서 비교함으로써 구조 진동 제어 문제에서 강화학습 제어기의 성능 특성과 한계를 규명하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 가장 단순한 비선형 제어로서 단자유도 가변 강성 시스템을 대상으로 심층 결정적 정책 경사(DDPG) 기반의 강화 학습 제어기를 설계하고, bang-bang 제어 및 제한 최적 제어와의 성능 비교를 수행하였다. 자유 진동 및 El Centro 지진 가속도에 의한 강제 진동 조건에서 공칭 성능과 센서 잡음이 존재하는 경우의 강인 성능을 분석하였다. 그 결과, 강화학습 제어기는 자유 진동 조건에서 우수한 강인 성능을 보였으나, 강제 진동 제어에서는 기존 제어기를 일관되게 상회하지는 못하였다. 이 연구는 동일한 보상 함수와 시스템 조건 하에서 강화학습 기반 진동 제어의 실질적 기여와 적용상의 한계를 기초적으로 제시하였다.
-
Performance Evaluation of Variable Stiffness Vibration Control for a Single-Degree-of-Freedom System Using DDPG Reinforcement Learning
-
Research Paper
-
Development of a GraphRAG-Based Automated Knowledge Graph Query Generation Model for Inference Search in BIM Data: A Case Study of a Rigid-Frame Bridge
BIM 데이터의 추론 검색을 위한 GraphRAG기반 지식그래프 질의 자동 생성 모델 개발: 라멘교를 중심으로
-
Hyunwoo Cha, Inwoo Jung, Hyounseok Moon
차현우, 정인우, 문현석
- Recently, Building Information Modeling (BIM) has evolved beyond three-dimensional modeling, increasingly focusing on the quality of standardized attribute data and systematic data …
최근 BIM은 단순 3차원 모델링을 넘어 표준화된 속성 데이터의 품질 확보와 체계적 관리가 핵심 요구로 부각되고 있으며, 온톨로지 및 지식그래프 기반의 데이터 …
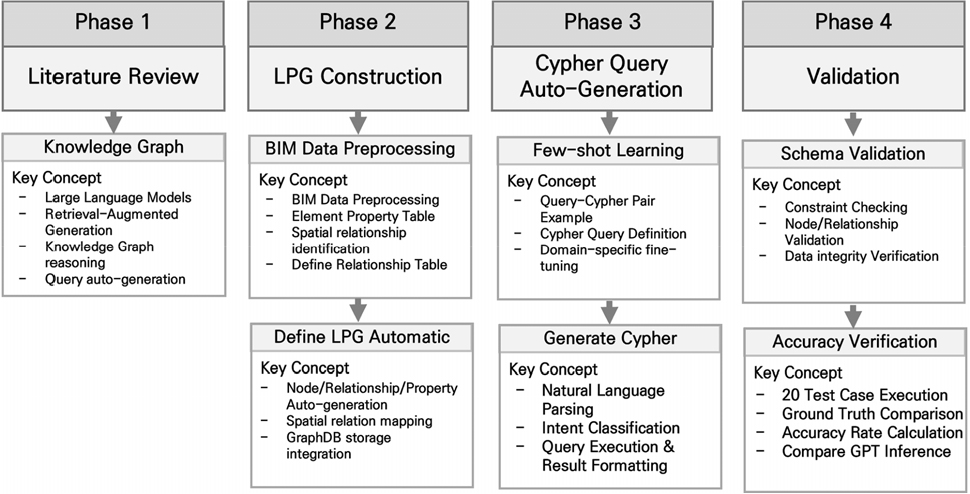
- Recently, Building Information Modeling (BIM) has evolved beyond three-dimensional modeling, increasingly focusing on the quality of standardized attribute data and systematic data management. Accordingly, ontology- and knowledge-graph–based data representation and reasoning approaches have increasingly gained attention. Knowledge-graph–based BIM data can support practical tasks such as structural relationship analysis, design review, and quantity and attribute information retrieval. However, practical adoption is limited by the need to manually write graph query languages, such as SPARQL and Cypher, which requires detailed knowledge of graph schemas and query syntax. To address this limitation, a GraphRAG-based automated query generation framework that converts natural-language questions into graph queries is proposed. A CSV-to-Labeled Property Graph (LPG) pipeline is developed to automate graph construction by generating nodes and relationships from rule-based attribute and relationship tables derived from bridge BIM data. In addition, a few-shot learning–based prompt design is utilized to generate Cypher queries from natural-language inputs automatically. The proposed framework is implemented as the Graph-ACQ system and validated using rigid-frame bridge BIM data. Experimental results demonstrate 100% accuracy in schema validity and query generation, with an average processing time of 7.1s. The proposed approach enables intuitive, relationship-oriented BIM data querying and supports scalable application across diverse infrastructure domains.
- COLLAPSE
최근 BIM은 단순 3차원 모델링을 넘어 표준화된 속성 데이터의 품질 확보와 체계적 관리가 핵심 요구로 부각되고 있으며, 온톨로지 및 지식그래프 기반의 데이터 관리・추론 방식이 주목받고 있다. 그러나 지식그래프 기반 BIM 데이터는 부재 간 구조 관계 분석, 설계 검토, 물량・속성 정보 조회 등 실무 의사결정을 지원할 수 있으나, SPARQL・Cypher와 같은 그래프 질의어를 직접 작성해야 한다는 점에서 실무 적용에 제약으로 작용한다. 이를 위해 본 연구에서는 사용자가 자연어 질문을 기반으로 그래프 질의를 자동 생성할 수 있는 GraphRAG 기반 질의 자동 생성 프레임워크를 제안하였다. 먼저 CSV 기반 속성/관계 테이블에 규칙을 적용해 노드・관계를 생성하고 그래프 데이터베이스에 적재하는 CSV-to-LPG 파이프라인을 구현하여, LPG 지식그래프 구축 절차를 자동화하였다. 이후 Few-shot Learning 기반 프롬프트 설계를 통해 사용자의 자연어 질문을 Cypher 쿼리로 자동 변환하는 자동 질의 생성 모듈을 구현하였다. 전체 프레임워크는 Graph-ACQ 시스템으로 개발하여 라멘교 BIM 데이터를 기반으로 적용하였다. 검증 결과 LPG 스키마 유효성과 Cypher 자동 생성, Cypher 질의 수작업 과정에서 정확도 모두 100%를 달성하였고, 질의 생성 시간은 평균 7.1초에 처리되었다. GraphRAG 기반 질의 생성 방식은 부재 간 공간・구조 관계를 명시적으로 활용하므로, 설계・검토 과정에서 요구되는 연결 관계 분석, 구조 구성 파악, 물량・속성 정보 조회 등 관계 기반 질의를 자연어로 수행할 수 있다. 또한 Few-shot Learning 기반 접근을 적용하여 교량 뿐만 아니라 다양한 공종 내에서도 질의 생성을 가능하게 함으로써, 프로젝트의 확장성을 확보 가능하다.
-
Development of a GraphRAG-Based Automated Knowledge Graph Query Generation Model for Inference Search in BIM Data: A Case Study of a Rigid-Frame Bridge
-
Research Paper
-
A Macro Model for Simulating Strength Degradation in Shear-Critical RC Columns
전단파괴형 RC 기둥의 내력저하 거동 재현을 위한 매크로 모델
-
Yousok Kim
김유석
- Shear failure followed by axial collapse in reinforced concrete (RC) columns with insufficient transverse reinforcement represens a critical structural failure mode. Conventional …
전단 보강근이 불충분한 철근콘크리트(RC) 기둥에서 발생하는 전단 파괴 및 이에 따른 축 붕괴는 매우 치명적인 파괴 유형이다. 기존의 모델들은 힘 모멘트-전단력-축력 간의 …
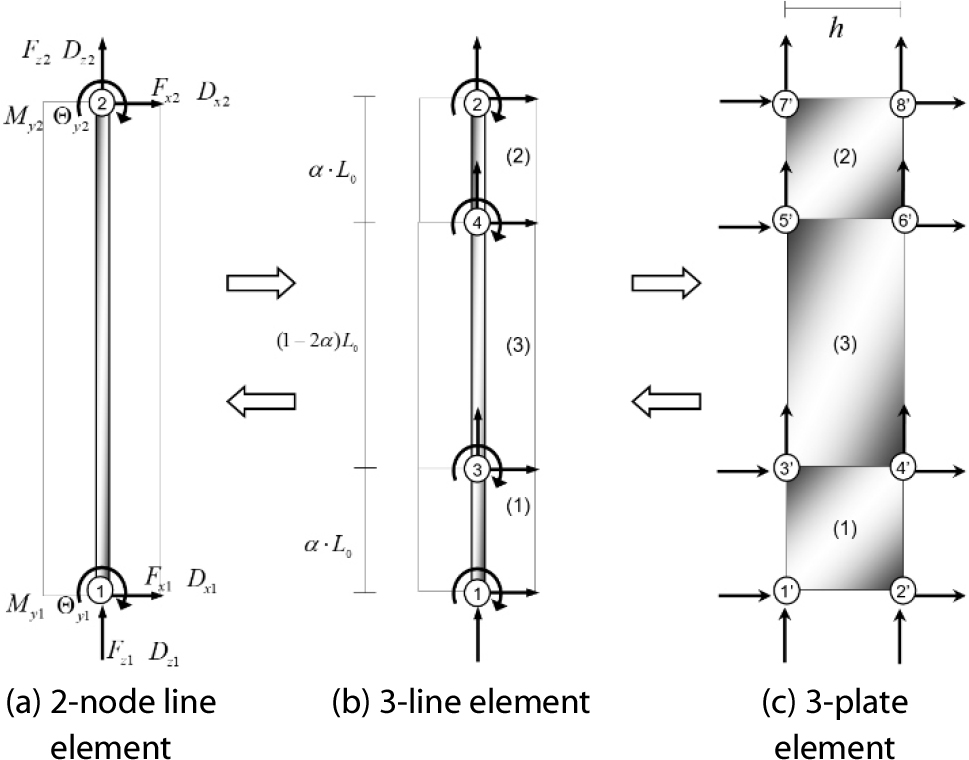
- Shear failure followed by axial collapse in reinforced concrete (RC) columns with insufficient transverse reinforcement represens a critical structural failure mode. Conventional analytical models often fail to accurately capture flexural-shear-axial interaction effects, whereas detailed finite element methods entail substantial computational cost. This study proposes a novel macro-element model that integrates material-level accuracy with the computational efficiency of line elements. The column is discretized into three elements along the longitudinal axis. Plate elements are formulated using a four-node plane-stress model incorporating the modified compression field theory (MCFT) to represent biaxial stress states and concrete compression softening. A double-nested iteration scheme is developed to satisfy equilibrium conditions. Validation against experimental data demonstrates that the proposed model accurately reproduces post-peak strength degradation and shear failure behavior, thereby addressing the key limitations of conventional fiber-based models.
- COLLAPSE
전단 보강근이 불충분한 철근콘크리트(RC) 기둥에서 발생하는 전단 파괴 및 이에 따른 축 붕괴는 매우 치명적인 파괴 유형이다. 기존의 모델들은 힘 모멘트-전단력-축력 간의 복잡한 상호작용을 모사하는 데 한계가 있는 반면, 정밀 유한요소해석법은 전체 골조 해석에 적용하기에는 연산 비용이 높다는 단점이 있다. 이에 본 연구에서는 재료 수준의 정밀도와 선요소의 해석 효율성을 결합한 새로운 매크로모델을 제안한다. 제안된 모델은 기둥을 3개의 요소로 분할한다. 면요소에는 수정 압축장 이론(MCFT)을 도입한 4절점 평면 응력 정식화를 적용하여, 콘크리트의 2축 응력 상태와 압축 연화(Compression Softening) 효과를 고려하였다. 또한, 해석의 수렴성과 평형 조건을 만족시키기 위해 이중 중첩 반복 계산 알고리즘을 개발하였다. 실험 데이터와의 검증 결과, 제안 모델은 기존 파이버 모델의 한계를 극복하고 최대 강도 이후의 내력 저하 및 전단 파괴 거동을 성공적으로 예측함을 확인하였다.
-
A Macro Model for Simulating Strength Degradation in Shear-Critical RC Columns
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea
Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea
Journal of the Computational Structural Engineering Institute of Korea











